lebedev_rule#
- scipy.integrate.lebedev_rule(n)[Quelle]#
Lebedev-Quadratur.
Berechnet die Abtastpunkte und Gewichte für die Lebedev-Quadratur [1] zur Integration einer Funktion über die Oberfläche einer Einheitskugel.
- Parameter:
- nint
Ordnung der Quadratur. Unterstützte Werte siehe Hinweise.
- Rückgabe:
- xndarray der Form
(3, m) Abtastpunkte auf der Einheitskugel in kartesischen Koordinaten.
mist der "Grad", der der angegebenen Ordnung entspricht; siehe Hinweise.- wndarray der Form
(m,) Gewichte
- xndarray der Form
Hinweise
Implementiert durch Übersetzung des Matlab-Codes von [2] nach Python.
Die verfügbaren Ordnungen (Argument n) sind
3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29, 31, 35, 41, 47, 53, 59, 65, 71, 77, 83, 89, 95, 101, 107, 113, 119, 125, 131
Die entsprechenden Grade
msind6, 14, 26, 38, 50, 74, 86, 110, 146, 170, 194, 230, 266, 302, 350, 434, 590, 770, 974, 1202, 1454, 1730, 2030, 2354, 2702, 3074, 3470, 3890, 4334, 4802, 5294, 5810
Referenzen
[1]V.I. Lebedev und D.N. Laikov. „A quadrature formula for the sphere of the 131st algebraic order of accuracy“. Doklady Mathematics, Bd. 59, Nr. 3, 1999, S. 477-481.
[2]R. Parrish.
getLebedevSphere. Matlab Central File Exchange. https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/27097-getlebedevsphere.[3]Bellet, Jean-Baptiste, Matthieu Brachet und Jean-Pierre Croisille. „Quadrature and symmetry on the Cubed Sphere.“ Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics 409 (2022): 114142. DOI:10.1016/j.cam.2022.114142.
Beispiele
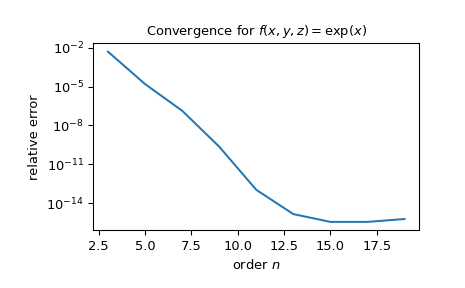
Ein Beispiel, das in [3] gegeben wird, ist die Integration von \(f(x, y, z) = \exp(x)\) über eine Kugel mit dem Radius \(1\); die Referenz dort ist
14.7680137457653. Zeigen Sie die Konvergenz zum erwarteten Ergebnis mit zunehmender Ordnung.>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> import numpy as np >>> from scipy.integrate import lebedev_rule >>> >>> def f(x): ... return np.exp(x[0]) >>> >>> res = [] >>> orders = np.arange(3, 20, 2) >>> for n in orders: ... x, w = lebedev_rule(n) ... res.append(w @ f(x)) >>> >>> ref = np.full_like(res, 14.7680137457653) >>> err = abs(res - ref)/abs(ref) >>> plt.semilogy(orders, err) >>> plt.xlabel('order $n$') >>> plt.ylabel('relative error') >>> plt.title(r'Convergence for $f(x, y, z) = \exp(x)$') >>> plt.show()