scipy.signal.windows.
boxcar#
- scipy.signal.windows.boxcar(M, sym=True, *, xp=None, device=None)[Quelle]#
Gibt ein Boxcar- oder Rechteckfenster zurück.
Auch bekannt als Rechteckfenster oder Dirichlet-Fenster, ist dies gleichbedeutend mit keiner Fensterung.
- Parameter:
- Mint
Anzahl der Punkte im Ausgabefenster. Wenn Null, wird ein leeres Array zurückgegeben. Bei negativen Werten wird eine Ausnahme ausgelöst.
- symbool, optional
Ob das Fenster symmetrisch ist. (Hat keine Auswirkung bei Boxcar.)
- xparray_namespace, optional
Optionaler Array-Namespace. Sollte mit dem Array-API-Standard kompatibel sein oder von array-api-compat unterstützt werden. Standard:
numpy- device: any
optionale Gerätespezifikation für die Ausgabe. Sollte mit einer der unterstützten Gerätespezifikationen in
xpübereinstimmen.
- Rückgabe:
- wndarray
Das Fenster, mit dem maximalen Wert auf 1 normalisiert.
Beispiele
Plotten Sie das Fenster und seine Frequenzantwort
>>> import numpy as np >>> from scipy import signal >>> from scipy.fft import fft, fftshift >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>> window = signal.windows.boxcar(51) >>> plt.plot(window) >>> plt.title("Boxcar window") >>> plt.ylabel("Amplitude") >>> plt.xlabel("Sample")
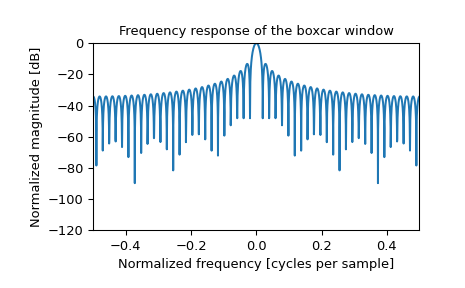
>>> plt.figure() >>> A = fft(window, 2048) / (len(window)/2.0) >>> freq = np.linspace(-0.5, 0.5, len(A)) >>> response = 20 * np.log10(np.abs(fftshift(A / abs(A).max()))) >>> plt.plot(freq, response) >>> plt.axis([-0.5, 0.5, -120, 0]) >>> plt.title("Frequency response of the boxcar window") >>> plt.ylabel("Normalized magnitude [dB]") >>> plt.xlabel("Normalized frequency [cycles per sample]")