lanczos#
- scipy.signal.windows.lanczos(M, *, sym=True, xp=None, device=None)[Quelle]#
Gibt ein Lanczos-Fenster zurück, das auch als Sinc-Fenster bekannt ist.
- Parameter:
- Mint
Anzahl der Punkte im Ausgabefenster. Wenn Null, wird ein leeres Array zurückgegeben. Bei negativen Werten wird eine Ausnahme ausgelöst.
- symbool, optional
Wenn True (Standard), wird ein symmetrisches Fenster zur Filterentwurf verwendet. Wenn False, wird ein periodisches Fenster für die Spektralanalyse generiert.
- xparray_namespace, optional
Optionaler Array-Namespace. Sollte mit dem Array-API-Standard kompatibel sein oder von array-api-compat unterstützt werden. Standard:
numpy- device: any
optionale Gerätespezifikation für die Ausgabe. Sollte mit einer der unterstützten Gerätespezifikationen in
xpübereinstimmen.
- Rückgabe:
- wndarray
Das Fenster, dessen Maximalwert auf 1 normiert ist (obwohl der Wert 1 nicht erscheint, wenn M gerade und sym True ist).
Hinweise
Das Lanczos-Fenster ist definiert als
\[w(n) = sinc \left( \frac{2n}{M - 1} - 1 \right)\]wo
\[sinc(x) = \frac{\sin(\pi x)}{\pi x}\]Das Lanczos-Fenster hat reduzierte Gibbs-Oszillationen und wird häufig zur Filterung von Klimazeitreihen mit guten Eigenschaften in der physikalischen und spektralen Domäne verwendet.
Hinzugefügt in Version 1.10.
Referenzen
[1]Lanczos, C., und Teichmann, T. (1957). Applied analysis. Physics Today, 10, 44.
[2]Duchon C. E. (1979) Lanczos Filtering in One and Two Dimensions. Journal of Applied Meteorology, Vol 18, pp 1016-1022.
[3]Thomson, R. E. und Emery, W. J. (2014) Data Analysis Methods in Physical Oceanography (Dritte Auflage), Elsevier, pp 593-637.
[4]Wikipedia, „Fensterfunktion“, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Window_function
Beispiele
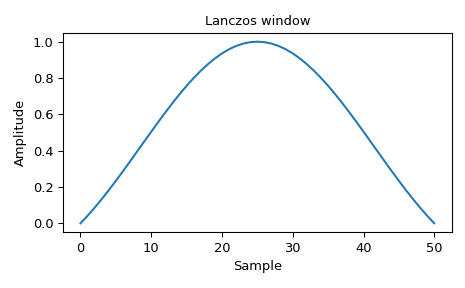
Zeichnet das Fenster
>>> import numpy as np >>> from scipy.signal.windows import lanczos >>> from scipy.fft import fft, fftshift >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> fig, ax = plt.subplots(1) >>> window = lanczos(51) >>> ax.plot(window) >>> ax.set_title("Lanczos window") >>> ax.set_ylabel("Amplitude") >>> ax.set_xlabel("Sample") >>> fig.tight_layout() >>> plt.show()
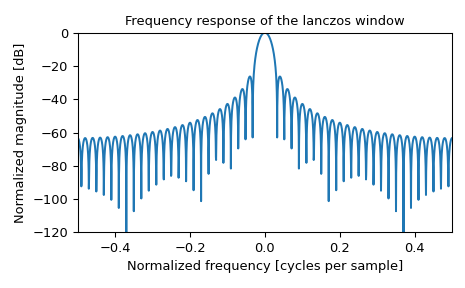
und seine Frequenzantwort
>>> fig, ax = plt.subplots(1) >>> A = fft(window, 2048) / (len(window)/2.0) >>> freq = np.linspace(-0.5, 0.5, len(A)) >>> response = 20 * np.log10(np.abs(fftshift(A / abs(A).max()))) >>> ax.plot(freq, response) >>> ax.set_xlim(-0.5, 0.5) >>> ax.set_ylim(-120, 0) >>> ax.set_title("Frequency response of the lanczos window") >>> ax.set_ylabel("Normalized magnitude [dB]") >>> ax.set_xlabel("Normalized frequency [cycles per sample]") >>> fig.tight_layout() >>> plt.show()