jnp_zeros#
- scipy.special.jnp_zeros(n, nt)[Quelle]#
Berechnet Nullstellen von Bessel-Funktionsderivaten Jn’ ganzzahliger Ordnung.
Berechnet nt Nullstellen der Funktionen \(J_n'(x)\) im Intervall \((0, \infty)\). Die Nullstellen werden in aufsteigender Reihenfolge zurückgegeben. Beachten Sie, dass dieses Intervall die Nullstelle bei \(x = 0\) ausschließt, die für \(n > 1\) existiert.
- Parameter:
- nint
Ordnung der Bessel-Funktion
- ntint
Anzahl der zurückzugebenden Nullstellen
- Rückgabe:
- ndarray
Erste nt Nullstellen der Bessel-Funktion.
Siehe auch
Referenzen
[1]Zhang, Shanjie und Jin, Jianming. „Computation of Special Functions“, John Wiley and Sons, 1996, Kapitel 5. https://people.sc.fsu.edu/~jburkardt/f77_src/special_functions/special_functions.html
Beispiele
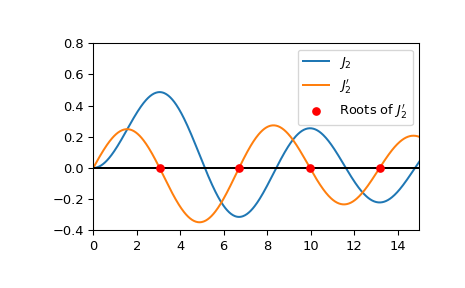
Berechnet die ersten vier Wurzeln von \(J_2'\).
>>> from scipy.special import jnp_zeros >>> jnp_zeros(2, 4) array([ 3.05423693, 6.70613319, 9.96946782, 13.17037086])
Da
jnp_zerosdie Wurzeln von \(J_n'\) liefert, kann es verwendet werden, um die Positionen der Maxima von \(J_n\) zu berechnen. Plottet \(J_2\), \(J_2'\) und die Positionen der Wurzeln von \(J_2'\).>>> import numpy as np >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> from scipy.special import jn, jnp_zeros, jvp >>> j2_roots = jnp_zeros(2, 4) >>> xmax = 15 >>> x = np.linspace(0, xmax, 500) >>> fig, ax = plt.subplots() >>> ax.plot(x, jn(2, x), label=r'$J_2$') >>> ax.plot(x, jvp(2, x, 1), label=r"$J_2'$") >>> ax.hlines(0, 0, xmax, color='k') >>> ax.scatter(j2_roots, np.zeros((4, )), s=30, c='r', ... label=r"Roots of $J_2'$", zorder=5) >>> ax.set_ylim(-0.4, 0.8) >>> ax.set_xlim(0, xmax) >>> plt.legend() >>> plt.show()