scipy.stats.
abs#
- scipy.stats.abs(X, /)[Quelle]#
Absolutwert einer Zufallsvariable
- Parameter:
- XContinuousDistribution
Die Zufallsvariable \(X\).
- Rückgabe:
- YContinuousDistribution
Eine Zufallsvariable \(Y = |X|\).
Beispiele
Angenommen, wir haben eine normalverteilte Zufallsvariable \(X\)
>>> import numpy as np >>> from scipy import stats >>> X = stats.Normal()
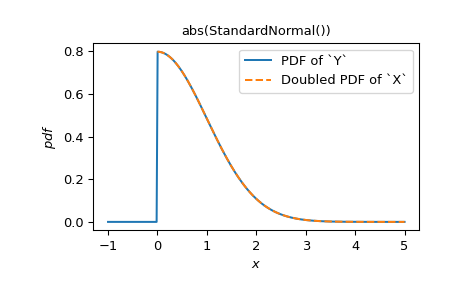
Wir möchten eine Zufallsvariable \(Y\) haben, die gemäß der gefalteten Normalverteilung verteilt ist; das heißt, eine Zufallsvariable \(|X|\).
>>> Y = stats.abs(X)
Die PDF der Verteilung in der linken Halbebene wird in die rechte Halbebene "gefaltet". Da die normale PDF symmetrisch ist, ist die resultierende PDF für negative Argumente Null und für positive Argumente verdoppelt.
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> x = np.linspace(0, 5, 300) >>> ax = plt.gca() >>> Y.plot(x='x', y='pdf', t=('x', -1, 5), ax=ax) >>> plt.plot(x, 2 * X.pdf(x), '--') >>> plt.legend(('PDF of `Y`', 'Doubled PDF of `X`')) >>> plt.show()